SDT 650同步热分析质谱联用仪成果展示
创建时间:2023-08-09 17:18:42
Recycling of silicon from waste PV diamond wire sawing silicon powders: A strategy of Na2CO3-assisted pressure-less sintering and acid leaching
(Qipeng Zou , Liuqing Huang , Weinan Chen , Guangyu Chen , Yan Li , Mengchen Li , Chentong Zhang , Xuetao Luo)
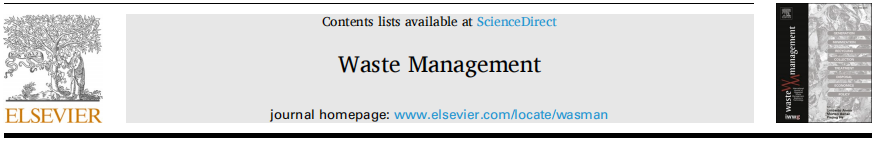
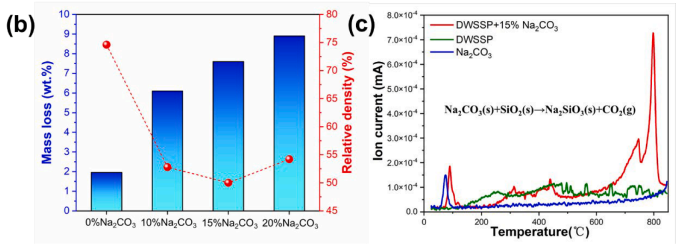
The mass loss rate and bulk density of the DWSSP-ceramics samples with various Na2CO3 content are presented in Fig. 3(b). The mass loss (1.96 %) of DWSSP-ceramic (0 % Na2CO3) was close to the content of C in DWSSP (1.71 %), indicating that the mass loss was predominantly from the removal of organic substances during the sintering process. Due to the gas evaporation, the mass loss rate of the DWSSP-ceramic with Na2CO3 sintering aid was proportional to the amount of Na2CO3 added. It was noted that the use of Na2CO3 sintering aid helped to decrease the relative density of ceramics. The relative density of DWSSP-ceramics decreased and then increased with the increase of Na2CO3 addition content and reached a minimum value of 50 % when the sintering aid content was 15 %. To determine the chemical composion of the gas, three samples (DWSSP, Na2CO3, and the mixture of DWSSP-15 % Na2CO3) were tested by TGA-MS. As shown in Fig. 3(c), it was found that the characteristic signals of CO2 gas (44 amu) were appeared at ~800 ℃ in the sample (DWSSP-15 %Na2CO3). It can be inferred that the released CO2 was generated during the reaction between Na2CO3 and SiO2 shell of DWSSP (Yang et al., 2020a,b,c). Therefore, it can be speculated that pores in the DWSSP-ceramics were formed during the sintering process due to the release of CO2 gas.

